TABLE OF CONTENTS
This match-up between cannabis-infused products is a close call. Each product has its unique advantages and disadvantages depending on your consumption preference or medical condition.
Here’s a rundown on the pros and cons of cannabis tinctures and edibles.
Cannabis Tinctures vs Edibles – What are They?
Technically, cannabis tinctures are edibles.
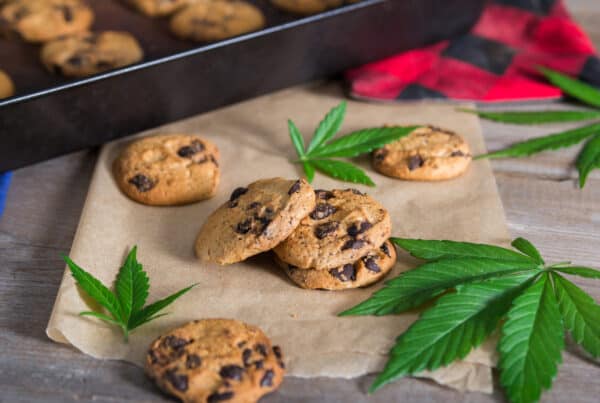
Edibles are cannabis-infused beverages, food, and other ingestible products that provide powerful and long-lasting relief. Common edibles include brownies, cookies, gummies, chocolate, pretzels, sugary drinks, and more.
Cannabis tinctures are alcohol or oil-based extracts that can be added to food and drinks or taken alone sublingually.
Edibles are made by using an infused cannabutter or canna-oil as a base ingredient. Cannabis flower or cannabis concentrates can be used to make edibles to replace the regular oil or butter in any recipe.
Both tinctures and edibles can be found in intoxicating and non-intoxicating products (THC and CBD, respectively). Whether you're looking for that buzz or clear-headed experience, tinctures and edibles have got you covered.
Now, the question is: which one is the best for you?
Oral vs Sublingual Consumption
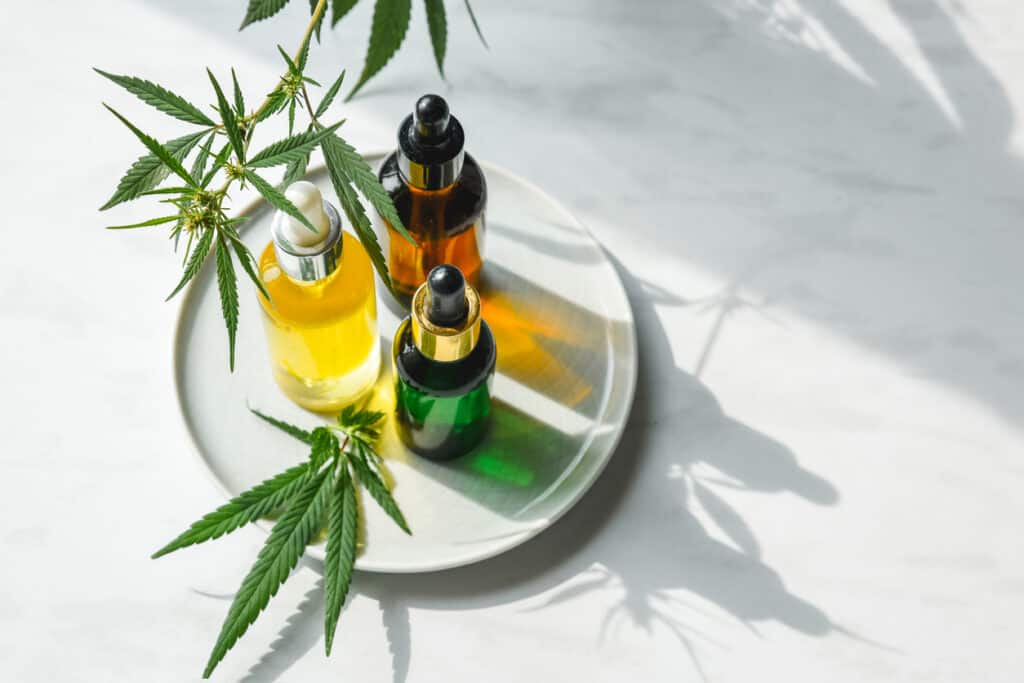

Cannabis can be consumed in a variety of ways. Choosing the right consumption method depends on your specific recreational or medicinal needs.
Here is a breakdown of the most popular consumption methods to help you make an informed decision.
Smoking and Vaping
Smoking and vaping are the most popular consumption methods and involve inhaling the smoke or vapor resulting from heating the flower or concentrate at relatively high temperatures.
Weed’s effects after inhalation appear in as little as five to 10 minutes. For instant relief, it’s hard to beat smoking a joint or taking a dab.
However, smoking and vaping cannabis is not the only or best method of consumption for every type of cannabis user. For instance, first-time or health-conscious users may want a smokeless consumption method that avoids introducing any harmful substances into their lungs. That is where cannabis tinctures and edibles come in.
Oral Consumption
Oral consumption occurs when you ingest a marijuana edible in the form of capsules, baked goods, drinks, and tinctures.
When consumed orally, the active compounds have to travel through the body’s digestive system to become metabolized and then released into the bloodstream. That is why the onset of effects takes longer when consuming edibles compared to smoking or vaping marijuana.
In the liver, cannabis’ THC compound converts into a metabolite (11-Hydroxy-THC) with stronger and longer-lasting effects than THC. If consuming CBD, most of the concentration of CBD is metabolized into 7-hydroxy-CBD.
Sublingual Consumption
Sublingual consumption, on the other hand, places the therapeutic compounds directly into the bloodstream without having to go through the digestive tract and the liver.
You can add a few drops (or more) of the tincture under your tongue for at least 20 seconds and wait until a good amount of cannabinoids have absorbed into your body. Then you swallow the tincture, which allows the digestive tract to absorb any remaining cannabinoids.
When taken under the tongue, tinctures have faster acting effects than edibles, which can take hours to kick in. In addition, you may feel a second onset of effects when the ingested cannabinoids have been metabolized.
Edibles, however, can provide slightly longer effects (up to eight hours) compared to the effects of tinctures which can last up to six hours. The longer-lasting effects can make all the difference for some users.
Cannabis Tinctures vs Edibles: Pros and Cons
Cannabis tinctures and edibles: which one is the best for you? There isn’t a straightforward answer to this question. What may be right for you may not be for another person. Consider these factors when choosing your infused product.
Convenience
In terms of convenience, both CBD tinctures and edibles are easy to carry in a purse, bag, or pocket. Unlike smoking, which requires a smoking device, a lighter, and flower, tinctures and edibles require no assembly. All you need to do is munch on some delicious snacks or add a few drops of tincture under your tongue.
Potency
In terms of potency, edibles and tinctures are hard to beat depending on how much you want to consume. Edibles, however, usually contain fewer total cannabinoids compared to tinctures, which can contain up to 1,000 milligrams of THC. If you are looking for those high concentrations and don't want to get full, tinctures are the way to go.
Dosing
When it comes to dosing tinctures and edibles, one is far easier to dose than the other. With tinctures, you can use a dropper featuring graduated mL indicators that can help you carefully dose the right amount and feel the effects almost instantly. Refer to the label instructions on the package for a recommended starting dose.
With edibles, dosing is much more difficult. Cannabinoid absorption can depend on if you take the edible after eating or on an empty stomach.
Eating edibles on an empty stomach can cause intense and unpredictable effects that can increase a person's anxiety and the side effects of the cannabinoid. Eating an edible after a meal can increase the onset of effects. In addition, what you eat can affect how well your body absorbs the cannabinoids.
However, edibles can provide longer-lasting effects on a single dose compared to using tinctures which may require more frequent doses throughout the day.
Safety
A big part of the popularity of edibles is their familiar form and taste. However, this can be a double-edged sword. In some cases, edibles can be confused with everyday food, including by children and pets. Accidental cannabis consumption can lead to severe side effects and hospital admission.
If using edibles, we recommend storing them in a safe place, similar to keeping alcoholic beverages away from reach. Whether you store them on the highest shelf or a drawer, it is important to keep them inside their original childproof container to add another layer of security.
Nutrition
Generally, tinctures have much lower calories, sugars, and fats compared to edibles. While a few doses of edibles are not significantly unhealthy, it is important to consider their nutritional value instead of just focusing on their effects. Tinctures provide you with a low-calorie and low-sugar alternative that enables you to consume less of these and still get considerable relief.
Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to the amount and rate of absorption of the active compounds in the body. When taken sublingually, tinctures can have a bioavailability between 40 to 50%.
When ingested, edibles can have a bioavailability between 4 to 20% due to the metabolizing process in the digestive tract. Generally, tinctures are more cost-effective due to the number of cannabinoids your body can absorb sublingually.
Which One Is Right For You? Edibles vs. Tinctures
Ultimately, the best type of cannabis product for you depends on a variety of factors including your metabolism, frequency of use, the amount used, potency, medical condition, and more. In some cases, both types of products can provide you with relief depending on the situation.
Edibles can be a nice treat to enjoy from the comfort of your home or with friends. They can be a fun and delicious alternative to tinctures on occasions where you want to treat yourself or experience longer-lasting relief.
Tinctures can go into nearly any food or drink so you can have any type of edible you want, technically. In terms of variety and versatility, tinctures can't be beaten. Tinctures are available in natural or flavored varieties so you can enjoy them alone or in your favorite food.
Fortunately, you don’t have to make a choice between the two. Often, using them synergistically can provide you relief in different situations. For longer relief, edibles can do the trick. If you want to supplement the effects of an edible, you can add some tincture drops under your tongue when the effects are wearing down.
Medical Application of Cannabis Tinctures vs Edibles
Cannabis can help treat a wide range of medical conditions and symptoms through many forms including whole-flower, concentrates, edibles, tinctures, and topicals.
Tinctures and edibles can provide you with a rush of energy, a dose of relaxation, and a dash of concentration. While these medicinal effects can be enjoyed recreationally, medicinal users may depend on cannabis’ therapeutic value to improve their quality of life.
For severe and debilitating pain and medical conditions, edibles can provide you with the high concentrations of cannabinoids (THC, CBD, and more) needed to make a dent in the pain, inflammation, and seizures for all-day relief. Instead of regularly dosing cannabis, you can consume a single edible dose to have relief for up to eight hours.
Cannabis edibles and tinctures can both help patients with everything from sleep problems to chemotherapy treatment.
Tinctures, however, can be easier to consume for those with appetite problems and nausea, as well as those who can’t eat as much or swallow as easily.
Medical users may opt for the concentrated tincture, which can be tasteless, sugarless, and make a great addition to a meal or a cup of tea.
The Storage of Cannabis Tinctures
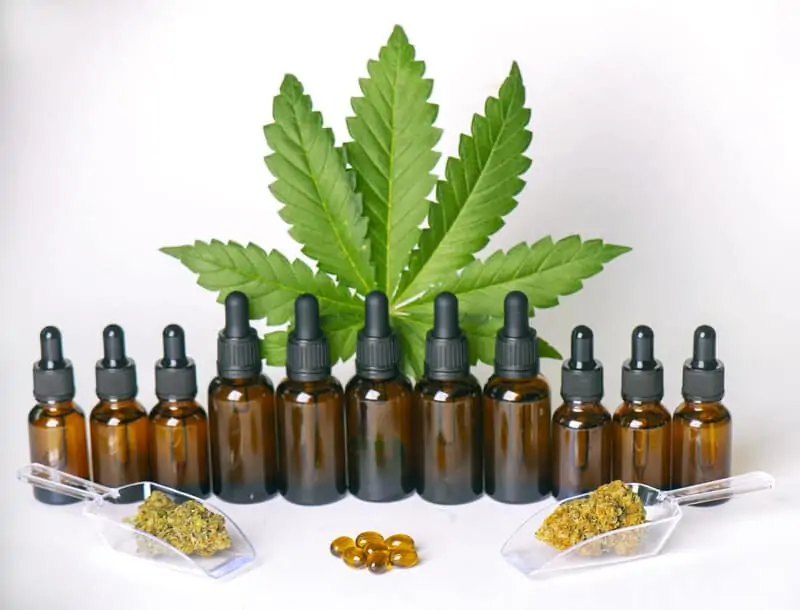

When stored, cannabis tinctures can last for a lot of years, especially if stored in a cool and dark place. Its long shelf life allows the user to store it in large quantities, making it convenient to have when you need it.
Using Cannabis Tinctures In Your Meals and Drinks
If you use alcohol of 190-proof in your cannabis tincture, you can expect seven calories for each milliliter. On the other hand, the typical brownie has an expectation of about 112 calories or even more. You can incorporate cannabis tinctures into your drinks and meals. This includes:
- Salad dressings
- Soups
- Ice creams
- Gravy
- Juices
- Salads
- Mashed potatoes
After cooking a meal of chicken and gravy, you could put some of your cannabis tincture in for a deliciously infused meal.
Learn More about Cannabis Delivery Methods at CTU
Interested in learning more about the differences and similarities between tinctures,edibles, and other infused products? Want to learn more about the cannabis plant, its cannabinoids and terpenes, the endocannabinoid system,and the many available products containing its therapeutic compounds?
Check out our blog/resource center for tips on how to make cannabis tincture and edibles, cannabis tincture/edible dosage, how to use cannabis tinctures and edibles, and cannabis tincture and edible side effects. Our informative articles can help you have a safe and effective experience.
For a complete cannabis education, sign up for CTU’s online cannabis college to learn how to use and grow cannabis, as well as how to get a rewarding career in this business.
Do tinctures get you high?
Yes, cannabis tinctures can get you high, depending on their THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) content. THC is the primary psychoactive compound found in the marijuana plant that is responsible for the feeling of being high. Tinctures are a form of concentrated cannabis extract that are typically taken sublingually (under the tongue) and are absorbed into the bloodstream quickly, resulting in a fast-acting and potent effect.
“
There are over 300,000 jobs in the cannabis industry. CTU trained me for one of them!

Makes $24.50 @ THC +
What is cannabis tincture used for?
Cannabis tinctures are commonly used for several purposes, including:
Pain relief: THC and CBD are both believed to have pain-relieving properties, and tinctures are a popular choice for those seeking relief from conditions such as arthritis, menstrual cramps, and headaches.
Anxiety and stress relief: THC and CBD are also known for their ability to promote relaxation and calmness, making tinctures a popular option for people dealing with anxiety and stress.
Sleep aid: Some people use tinctures to help them fall asleep and stay asleep, as THC and CBD can both promote sleep and have sedative effects.
Appetite stimulation: THC is known for increasing appetite, and tinctures are often used by people undergoing cancer treatments or those with other conditions that cause a loss of appetite.
Are tincture stronger than edibles?
The strength of a tincture and an edible can vary greatly depending on factors such as the potency of the product, the dose consumed, and the individual's tolerance and metabolism.
Tinctures are typically made by infusing alcohol or another solvent with cannabis and are designed to be taken sublingually, meaning under the tongue. Because the compounds are absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the tissues in the mouth, tinctures can take effect more quickly than edibles, which have to be digested before they can be metabolized. This means that the onset of effects can be quicker and the effects can be more intense than with edibles.
However, the strength of a tincture also depends on the potency of the product, and some tinctures can be more potent than others. The same is true for edibles, as the potency can vary greatly depending on factors such as the recipe and the quality of the ingredients used.
What is stronger, cannabis oil or tincture?
The potency of cannabis oil and tincture can vary depending on the production method and the amount and type of cannabinoids they contain. In general, the potency of cannabis oil is higher than that of a tincture because oil has a higher concentration of active ingredients. However, the potency can also depend on factors such as the strain of the plant used to produce the oil or tincture, the method of extraction, and the method of administration.

Karen Getchell
Karen gained expertise in developing training programs and technical documentation as a Senior Editor at Cisco Systems. She began her journey in cannabis as a patient, searching for a way to heal herself. When she perfected a method for making cannabis oil, other patients began to seek her out. An early adopter of CBD medicine, she started her CBD-infused-products business in 2014. Over the last two decades, Karen has taught hundreds of patients and caregivers how to select strains, infuse oils, and extract cannabinoids.
When she isn’t teaching cannabis cooking classes, Karen works as a cannabis business consultant, writes for online cannabis publications like Cannabis Training University, Leafly, and Weedmaps, and runs a CBD-infused-product business.











 Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons
Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons  100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.
100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.