TABLE OF CONTENTS
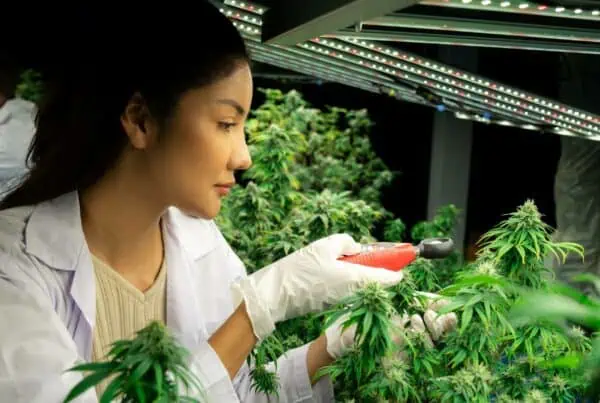
Hydroponic and aquaculture operations are combined in the gardening approach known as aquaponics.
It is a method of growing marijuana that involves the two effective and efficient systems, combing each of them so they can work to benefit each other.
An Introduction to Aquaponic Cannabis Growing
With good reason, aquaculture is swiftly gaining popularity among indoor gardeners as one of the most effective ways to grow cannabis harvests at home or commercially.
It's understandable why so many growers like this method over more conventional farming practices like hydroponics or soil culture methods given its low environmental effect and flexibility in setups to suit individual demands and budgets.
In addition to being more environmentally friendly than other techniques, aquaponics costs less and enables growers to tailor their system to the sort of cannabis they are cultivating.
Fish excrement serves as a natural supply of plant fertilizer in this process, and plants also filter and purify the water used in the system.
The health and prosperity of the plants and the fish are both guaranteed by this symbiotic interaction.
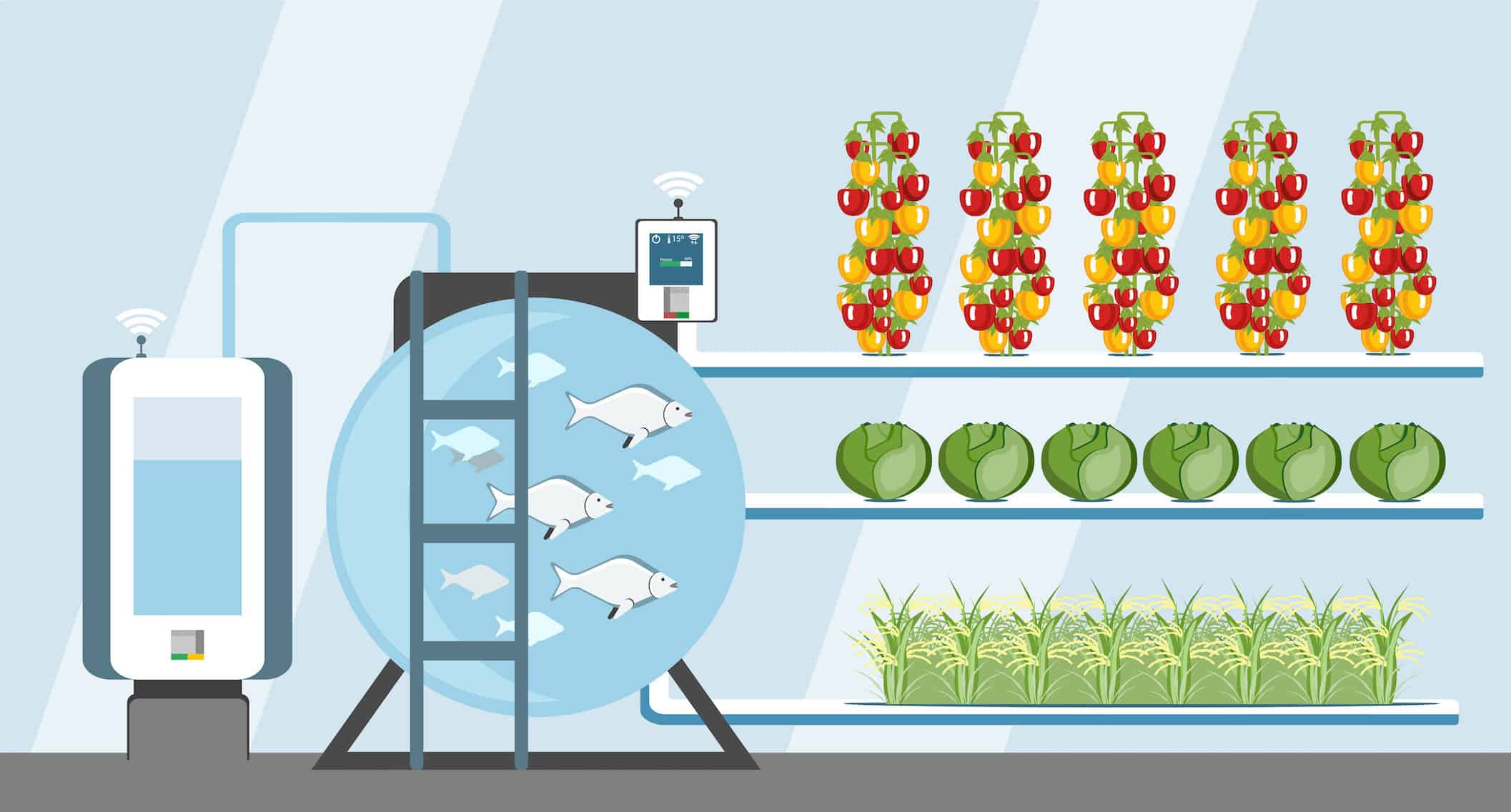
An aquaponic system's primary components include fish tanks, plant beds, pumps, and bio-filters. It's critical to select a size for your aquaponic cannabis growing system that meets your needs and budget.
Cannabis Aquaponic Growing Systems: Benefits
The use of an aquaponic system for cannabis cultivation has several benefits. It is considerably simpler to uphold organic standards while growing cannabis in an aquaponic system because there is no soil involved in the process, which reduces the chance of contamination from pesticides or fertilizers used on conventional farms or greenhouses.
Additionally, these systems have a substantially smaller environmental impact than typical agricultural operations because they utilize up to 90% less water than traditional farming techniques.
Finally, producers may easily select the system that will work best for them because these systems can be tailored to meet unique needs and financial constraints.
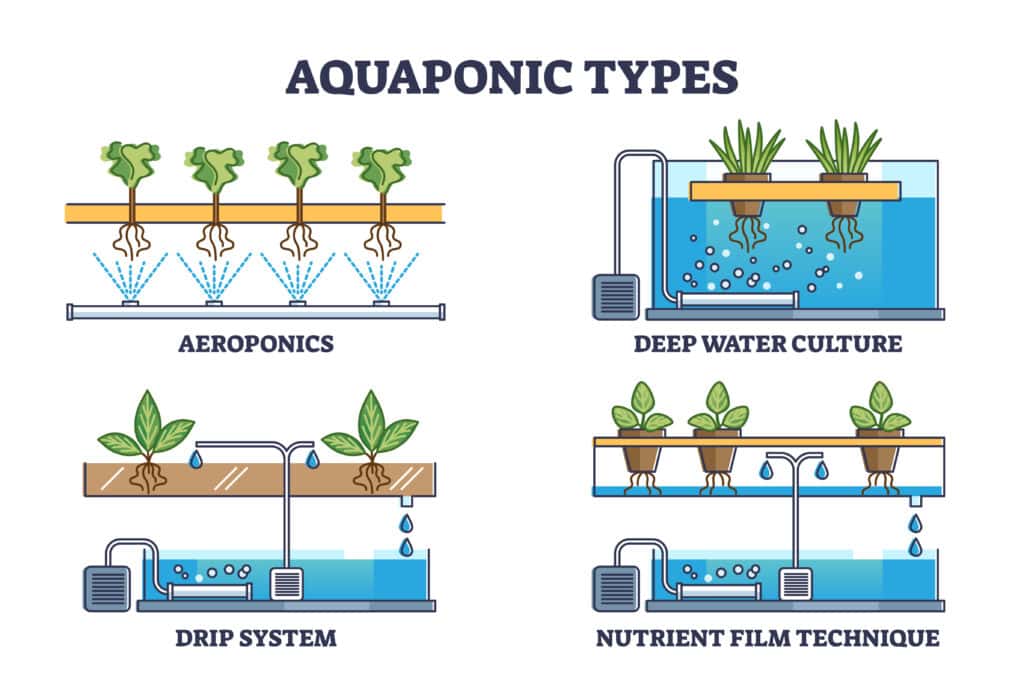
The Aquaponic Systems and How it Works
You would use a double root zone to set your system. The bottom half can be filled using hydroponic means or you can suspend the roots in water. The aquaponic system and hydroponic system are almost identical in many ways.
The primary difference is the nutrient source. In this process, no nutrients are added to the water tank, but rather, you would produce them using the waste of the fish. The waste would be diluted and pumped and placed on the roots of the marijuana plant.
The roots will absorb those nutrients and believe it or not, the water will be purified prior to it returning to the aquarium. The only input that you will need is fish food. You can grow this yourself or buy it locally.
The Nutrient
The main nutrient that the fish waste will produce is nitrogen and this nitrogen will have traces of other minerals.
For cannabis, you are going to need added nutrients such as potassium and phosphorus. The double root zone provides the remedy. What is a double root zone?
The Double Root Zone (Dual Root Zone)
You will be able to divide the roots by section with the double root zone. The bottom half of your pot has to be submerged into the water while you fill the upper half with soil. By doing this, you will permit the added nutrients to be effectively applied to your roots so that the water is not contaminated.
You will have divided the roots into two sections and then separate these sections by using burlap. This allows your roots to travel through as the soil is prevented from reaching the water. When you are giving your plants water with the added cannabis growing nutrients, be sure not to saturate the soil too much because it is important that the water in your aquaponic system is kept clean at all times.
Aquaponics vs Hydroponics vs Aeroponics
Aquaponics, Hydroponics, and Aeroponics are three types of soilless agriculture systems used for growing plants.
Aquaponics is a system where fish and plants are grown in a symbiotic relationship, where the fish waste provides nutrients to the plants and the plants help to purify the water for the fish.
Hydroponics is a system where plants are grown in nutrient-rich water instead of soil.
Aeroponics is a system where plants are grown in air or mist and their roots are suspended in the air.
Aquaponics vs Soil
In terms of growth rate, hydroponics and aeroponics can have faster growth rates than aquaponics and soil-based farming, but this also depends on many other factors such as light, temperature, and nutrient levels.
Aquaponics vs Hydroponics Yield
The yield of hydroponics and aquaponics can be higher than traditional soil-based farming, but again, this depends on many factors.
In conclusion, each of these systems has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which to use depends on various factors such as the type of plant, the environment, and the goal of the grower.
How Does Aquaponics Compare to Traditional Farming?
Aquaponics is a hybrid farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish or other aquatic animals) with hydroponics (growing plants in water without soil).
Compared to traditional farming, aquaponics has several benefits:
Efficiency: Aquaponics uses less water and land compared to traditional farming, making it a more sustainable option.
Climate Control: The controlled environment of an aquaponic system allows for year-round food production, regardless of weather conditions.
Reduced Pesticides and Herbicides: As the system is closed and self-contained, the use of harmful chemicals is minimized.
Increased Yields: The controlled environment and constant supply of nutrients to the plants result in faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional farming.
However, there are also some challenges associated with aquaponics, such as the need for a steady supply of energy to maintain the water temperature and pump water, and the higher upfront costs of setting up an aquaponic system.
Common Questions Regarding Aquaponics for Cannabis Growing
What nutrients does aquaponics lack?
Although potassium may require additional supplementation depending on plant requirements & pH levels within the tank/system overall, all three major macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) should generally be present in adequate amounts in any properly functioning aquaculture/aquarium setup. If you notice deficiencies, adding specific supplements can help correct them.
Do worms in aquaponics drown?
Earth worms have unique adaptations that allow them to breathe underwater, therefore they rarely drown in well-oxygenated systems. However, if oxygen levels fall too low, they could eventually suffocate and pass away.
How frequently should water be changed in aquaponics?
In general, depending on size and arrangement, most systems need a full water change every 4-6 weeks. However, some bigger commercial setups may go longer between changes due to filtration capabilities.
“
There are over 300,000 jobs in the cannabis industry. CTU trained me for one of them!

Makes $24.50 @ THC +
How much light is required for aquaponics?
Most light cycles should be between 12 and 18 hours each day, depending on the type or variety of plants being produced.
How frequently should aquaponics be flooded and drained?
Depending on the size of your grow bed or grow beds, anywhere from 2-4 times each day should be sufficient.
What depth is ideal for an aquaponic grow bed?
Ideal depth is 12 to 18 inches, however this might change based on the type and variety of plants being cultivated, the weather, the outside temperature, and other factors.
Ready to Start Your Own Aquaponic Cannabis Grow System?
Now that we've explained how the aquaponic cannabis grow method functions and addressed some frequently asked questions, you're prepared to begin growing top-notch aquaponic buds right away!
Learn more about growing marijuana indoors.

Luis Cordova
Luis Cordova is a distinguished author, and renowned expert in cannabis cultivation, who possesses a Master's degree in Plant Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Science. As a valued contributor to highly esteemed publications such as Cannabis Training University and Maximum Yield Magazine, Luis has emerged as a trusted source of guidance and knowledge in the cannabis industry. Having written thousands of informative articles, Luis is widely recognized for his comprehensive expertise on cultivating cannabis, both indoors and outdoors.












 Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons
Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons  100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.
100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.