
Certification included when you enroll
in the online ©Master of Cannabis Program!
 Medical Marijuana
Medical Marijuana 
In this course, included in the Master of Cannabis Program, you will learn everything about using marijuana as medicine. You will gain caregiver skills, as well as information on how to help guide cannabis patients. In this course you will learn about different strains and how they can be used to help treat different diseases, cannabis administration, dosage, titration, side effects, drug interaction, the endocannabinoid system, and more!
In this course, learn everything about using marijuana as medicine. Gain caregiver skills and how to help guide cannabis patients. Learn about different strains and how they can be used to help treat different diseases, cannabis administration, dosage, titration, side effects, drug interaction, the endocannabinoid system, and more!
FAQs
Is this cannabis college accredited?
Yes! We are the only cannabis education school in the world that has an internationally recognized accreditation provided by ANSI/IACET.
Is this certification included in the Master of Cannabis Program?
Yes! This certification, and 9 other certificates are included in the Master of Cannabis Program.
Is this online or in person?
It is 100% online. You can make your own schedule, and work from any device!
How long does it take to complete the Master of Cannabis Program?
Complete the required work in as little as 7 days (42 hrs of required content), or take your time (24 weeks of access) and enjoy hundreds of hours of how-to tutorials, resources, and 8 Ed Rosenthal e-books. There are no set class times and no homework, and anyone 18+ can enroll. If you need more time in the program it is easy to extend your access!
If you want to stay on the legal side, there is a way to pursue it. That’s the training you get from the Cannabis Training University.
– Kevin O’Leary
Businessman

Medical Marijuana Certification: Topics
Cannabis Basics
What Is Cannabis?
Cannabis has been described as a weed, as a recreational drug, and as the latest craze in medical treatment. But what actually is it? This lesson will cover the origins of the cannabis plant and tell you what you need to know about cannabis strains and cultivars. The lesson covers these topics:
- Cannabis Plant Overview, including Origins of Cannabis, Cannabis Cultivars, Cannabis Strains, Descriptions of Cannabis Sativa,
 Cannabis Indica, Hybrids, and Cannabis Ruderalis, Parts of the Cannabis Plant, Cannabis Seeds, Hemp Fiber, Cannabis Flowers, Cannabis Buds, Cannabis Nugs, and Cannabis Trichomes
Cannabis Indica, Hybrids, and Cannabis Ruderalis, Parts of the Cannabis Plant, Cannabis Seeds, Hemp Fiber, Cannabis Flowers, Cannabis Buds, Cannabis Nugs, and Cannabis Trichomes - The Difference Between Cannabis and Hemp
- Structure, Life Cycle, and Reproduction System of Cannabis Plants
- Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System
Components of Cannabis
A deep dive into compounds like THC, CBD, terpenes, and other components in cannabis that can have an impact on patients. The lesson covers these topics:
- The Primary Chemical Compounds in Cannabis, including Terpenes and Cannabinoids
- Entourage Effects of Cannabis Components
- Reasons to Use Cannabis Strains with THC, CBD, CBG, CBN, CBC, THCV, Beta Caryophyllene, Myrcene, Humulene, Alpha Pinene, Limonene, and Linalool
- Reasons to Avoid Cannabis Strains with THC, CBD, CBG, CBN, CBC, THCV, Beta Caryophyllene, Myrcene, Humulene, Alpha Pinene, Limonene, and Linalool
- THC Use with a Suppressed Endocannabinoid System (ECS), High Blood Pressure, Anxiety, Memory Issues
- Psychoactive Effects of THC, CBN, and THCV

- Dosing with THC, including Biphasic Effects
- THC Benefits for Mental State, the Nervous System, Inflammation, Cancer, Digestion, the Circulatory System, and Intraocular Pressure
- CBD Effects on Endocannabinoid Production and as a Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI)
- CBD Interaction with Chemotherapy, 5-HT1A Receptors, TRPV1-2 Vanilloid Receptors, AEA, Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes, and Drug Metabolization
- CBD Health Benefits for Blood Pressure, Healing the Gut, Epilepsy, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Diabetes, Appetite, Anxiety (Including THC-Induced Anxiety), Eating Disorders, Mental States, the Nervous System, Inflammation, Cancer, Digestion, Circulation, Skin Treatments, and Bone Growth
- CBN Medical Benefits for Sleep, Glaucoma, the Nervous System, Inflammation, Cancer, Appetite, Bone Growth, and the Eyes
- Health benefits of the Primary Cannabinoid CBG for Blood Pressure, Memory, Glaucoma, Inflammation, Mental Effects, the Nervous System, Cancer, IBS, Appetite, the Circulatory System, Psoriasis, and Bone Growth
- Health Benefits of CBC for Depression, Anxiety, Pain, Alzheimer’s Disease, Inflammation, Cancer, Acne
- Health Benefits of THCV for the Immune System, Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, Motor Control, Diabetes, Anxiety, Energy, Appetite Suppression, Epilepsy, Inflammation, and Bone Growth
- Monoterpenes and Sesquiterpenes
- The Presence of Terpenes in Cannabis Strains
- Terpenes and Infections (including MRSA)
- Beta Caryophyllene in Haze, Girl Scout Cookies, Skywalker OG, and Chem Dawg Strains
- Health Benefits of Beta Caryophyllene for Alcohol Addiction, Autoimmune Disorder, the Kidneys, Sleep Disorders, Reducing Cravings, Depression, as a Local Anesthetic, Depression, Inflammation, Cancer, the Digestive System, and IBS
- Myrcene in Indica Strains Like White Widow, Himalayan Gold, and Jack Herer
- Medicinal Benefits of Myrcene for Diabetes, Insomnia, Transdermal Absorption, Inflammation, Depression, Pain, and Cancer
- Alpha Pinene in Jack Herer Strain
- Alpha Pinene in Blue Dream, Trainwreck, Island Sweet Skunk, Romulan, Strawberry Cough, and Bubba Kush Strains
- Health Benefits of Alpha Pinene for Asthma, Alertness, Short-Term Memory, Pain, Inflammation, Cancer, and as a Bronchodilator
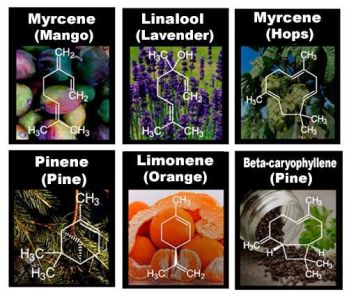
- Humulene in White Widow, Headband, and Sour Diesel Strains
- Medical Benefits of Humulene for Appetite, Transdermal Absorption, Inflammation, Cancer, and Pain
- Limonene in Super Lemon Haze, Pineapple Express, and Sweet Tangerine Strains
- Limonene Effects on A(2A) Receptors and Dopamine
- Health Benefits of Limonene for Anxiety, Depression, Mood, Absorption, Inflammation, Cancer, Gallstones, GER, and Acid Reflux
- Linalool in Lavender, Diamond Girl, and LA Confidential Strains
- Medicinal Benefits of Linalool for Nausea, Sleep, Anxiety, Depression, Pain, Seizures, Breast Cancer, Inflammation, and Acne
- Raphael Mechoulam and S. Ben-Shabbat’s Entourage Effect Research with Full Spectrum Medical Cannabis and Whole Plant Cannabis Medicine
- CBD and THC Interaction and Ratios
- Cannabis Entourage Effects on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Appetite, Memory, Attention, Insomnia, Sleep, and Addiction
- Cannabis Strains that Reduce Cravings, Increase Alertness, Improve Circulation, and Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cannabis Entourage Effects for Acne, Alzheimer’s Disease, Reducing Anxiety, Autoimmune Disorders, Lowering Blood Pressure, Mending Broken Bones, Cancer, Crohn’s Disease, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Ulcers, Depression, Diabetes, Epilepsy, Glaucoma, Inflammation, Muscle Spasms, Nausea, Neurological Damage, Pain Relief, Sleep, and Insomnia
- Synthetic Cannabis and THC Analogs (like Spice and K2) Used as Pharmaceuticals, as Recreational Drugs, and for Research on Tumors, Inflammation, and Blood Flow
Cannabis Products
The cannabis industry is growing exponentially. With growth comes a variety of new products—so many, in fact, that choosing the right one can be confusing to both new and experienced users. This lesson breaks down the most common products available at dispensaries. The lesson covers these topics:
- Differences between Cannabis Products, including Cannabinoid Content, Potency, Activation (Raw vs. Decarboxylated), Classification based on Strain Names or Cultivars, Classification Based on Indica, Sativa, or Hybrid, Terpene Content
- CBD:THC Ratio, THC-Dominant Products, CBD-Dominant Products, Hemp Products, 1:1 CBD:THC Ratios, CBD Products

- How Potency is Shown on Labels for Cannabis Flower, Cannabis Concentrates, and Edibles, including Percentages and Number of Milligrams
- Raw Cannabinoids, including THCA, CBDA, and Non-Activated Products
- How to Read Cannabis Product Labels, including Tracking and Regulatory Information, Effects, Cannabinoid Content, Activation Status, Potency, Contaminants, Nutrition Information, and Terpene Content
- Products Sold at Dispensaries, including Flowers, Concentrates, Edibles, Topicals, Transdermals, and Other Infused Products
- How to Find High Quality Top Shelf Bulk Cannabis Flowers, Buds, Joints, Blunts, Pre-Rolls, and Shake including Bud Size and Potential Cannabis Contaminants, Pesticides, Mold, and Seeds
- Characteristics of Low Quality Cannabis, including Scent, Color, Finger Feel, Throat Feel
- Cannabis Flower Consumption Methods, including Smoking and Vaporizing
- Input Materials for Cannabis Extracts, including Flash-Frozen Fresh Plants, Dried Cannabis Flowers, Dried Cannabis Trim, and Hemp
- Cannabis Extraction Methods, including Solventless Concentrates (Kief, Bubble Hash, Pressed Hashish, Rosin) and Solvent-Based Extracts (RSO, BHO, PHO, Ethanol Extracts, CO2 Oil, Distillate, Isolate, Water-Soluble Isolate, Nano-Isolate)
- Cannabis Concentrate Product Consistencies, including Budder, Shatter, Crumble, Wax, Live Resin, Sugar, Rocks and Sauce, and Vape Cartridges
- How Cannabis Edibles Work, including LDL Delivery, Liver Metabolites, Dosing, Digestive System Issues, and Sublingual Delivery
- Ingredients in Cannabis Edibles, including Flower Infusions in Oil, Distillates, Isolates, Full-Spectrum Extracts, Broad-Spectrum Extracts, Non-Cannabis Ingredients, and Allergens
- Differences between Full-Spectrum cannabis oil, Broad-Spectrum hemp oil, Cannabis Distillates, Isolates, and Nano-Isolates
- Cannabis Edibles, including Cannabis-Infused Oils, Cannabis Tinctures, Raw Cannabis Tinctures, Cannabis-Infused Capsules, Cannabis-Infused Foods, Gummies, Hard Candies, Savory Edibles Cookies, Brownies, Cannabis-Infused Beverages (Soda, Coffee, Tea, Beer, Energy Drinks)
- Cannabis Concentrates and Their Consumption, including Vaporizing with Vaporizers, Earth Stones, and Pens, How to Dab, and Dab Equipment (Dab Rigs, Nails, E-Nails, Torches, Dab Tools, Domes, Carb Caps, Terp Pearls, Quartz Inserts, Reverse Tweezers, Bangers)
- Cannabis-Infused Topical and Transdermal Products, including Creams, Lotions, Balms, Patches, and Roll-Ons
- Cannabis Topicals and Skin Sensitivity, Antioxidant Properties, Antimicrobial Properties, Acne Treatment, Onset and Duration, Pain Reduction, Inflammation Treatment, Itch Medicine
- Other Dispensary Products including Cannabis-Infused Inhalers, Bath Bombs, Sexual Lubricants, Suppositories, Sublingual Strips, Moon Rocks, Infused Joints, Shampoo, Topicals
Cannabis As Medicine
History of Medical Cannabis
A look at the origins of cannabis as medicine, and how the practice has evolved to meet the needs of modern patients. The lesson covers these topics:
- Ancient History of Hemp Cultivation
- Health Benefits of Cannabis, including Cannabis in the US Pharmacopoeia and Cannabis Used as a Legal Medicine

- Cannabis Legislation in the United States, including the 1914 Harrison Act, the Cannabis Tax Act, the Boggs Act, the Narcotics Control Act, the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act, the Shafer Commission, the Compassionate Investigational New Drug (IND) Program (also known as the IND Compassionate Use Program), the Controlled Substance Act, the 1986 Anti-Drug Abuse Act, the Cole Memo, Medical Cannabis Organ Transplant Act, FDA Approval of Marinol
- Public Cannabis Research Studies by Organizations Like the American Medical Association, the American College of Physicians, and the New England Journal of Medicine, including Scientific Evidence for Treating Glaucoma and Cancer with Cannabis
- Cannabis Regulation in the United States, including Cannabis Policy in the 1900s and 2000s, Ronald Reagan’s War on Drugs, the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA), Cannabis and the FDA, Mandatory Minimum Sentences for Cannabis
- Synthetic Cannabis Medicines like Dronabinol (Marinol) and Nabilone (Cesamet)
- Legal Medical Cannabis in California, Arizona, and Other States
- United States Political Policy on Pot, including legislation by former US Attorney General Jeff Sessions, former Presidents Ronald Reagan and Donald Trump, and former California Governor Jerry Brown
- Current Cannabis Policy In President Joseph Biden's Administration
- History of Cannabis Research on Phytocannabinoids, Cannabis and Pain, Cannabinol (CBN), Cannabidiol (CBD), Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), Cannabigerol (CBG), Cannabichromene (CBC), Cannabicyclol (CBL), Acid Forms of Cannabis (THCA, CBDA, CBGA, CBCA, and CBLA), Cannabinoid Receptors, CB1 Receptors, Cannabis Receptors in the Brain, Endocannabinoids, Endogenous Cannabinoids, Anandamide (AEA), N-Arachidonoyl Ethanolamine, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
- United States Patient Discrimination and Hypocrisy about Medical Cannabis
- The Research of Famous Cannabis Researchers like Thomas Wood, B. Rael Cahn, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, Allyn Howlett
- Cannabis Activist Groups and Groups for Cannabis Reform, including the National Organization for the Reform of Cannabis Laws (NORML), Americans for Safe Access (ASA), and Cannabis Policy Project (MPP)
- Physician Concerns about Cannabis, including Cannabis Abuse, Cannabis vs. Morphine, Patients and Medical Cannabis, First Amendment Rights for Doctors Prescribing Cannabis, Prescribing Cannabis as a Federal Crime, Prosecution of Doctors for Prescribing Cannabis
Medical Cannabis Programs in the United States and Canada
This lesson describes qualifying conditions, patient/caregiver registration, and limits for every US state with a medical cannabis program and Canada. The lesson covers these topics:
- Qualifying Conditions for Medical Cannabis in the United States

- Registering as a Medical Cannabis Patient in every US state with a medical cannabis program
- Registering as a Medical Cannabis Caregiver in every US state with a medical cannabis program
- Possession and Cultivation Rules for Medical Cannabis Patients in every US state with a medical cannabis program
- Canada’s Medical Cannabis Program, including Qualifying Conditions, Becoming a Patient with Health Canada, Purchasing Medical Cannabis, and Becoming a Caregiver
The Endocannabinoid System
Information on how the body’s endocannabinoid system reacts with cannabinoids found in cannabis, and the benefits they can provide. The lesson covers these topics:
- History of Mammals and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
- Cannabis and Homeostasis in the Human Body’s Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
- Using Cannabis for Optimum Health and to Maintain a Healthy Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
- The Lack of Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Education in Medical Schools

- How CB1 and CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Work Throughout the Cells of the Body
- How the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Regulates Stress, Appetite, Pain, Memory, Mood, Energy, Metabolism, Immune Function, Female Reproduction, the Autonomic Nervous System, Temperature Balance, and Sleep
- Plant Cannabinoids (Phytocannabinoids) and Endocannabinoids
- Cannabis and the Central Nervous System (CNS), including the effects of Cannabis on Brain Trauma, Spinal Cord Injury, Strokes, Neurotransmitter Uptake, and the Brain
- Naturally Occurring Cannabinoids such as Anandamide, 2-AG in the Human Body, Cacao, Black Pepper, Echinacea, and Kava
- CB1 Receptors interaction with Topicals, Anxiety, Happiness, Convulsions, Pain, Mood Regulation, Inflammation, Movement, Traumatic Memory, Nerve Protection, Bone Growth, Tumor Regulation, Breast Feeding, Eye Pressure, the Digestive System, and Seizures
- CB2 Receptors Interactions in the Liver and Skin and with Inflammation, the Immune System, Injury, Appetite, Pain, Mood, and Memory
- GPR55 G-Protein Receptor Interactions with CNS Inflammation and Pain, Embryos, Inflammation, Blood Vessels, Blood Movement, Bone Resorption, Kidneys, and Cancer
- Other Cannabinoid Receptors such as GPR18 G-Protein Receptors, Glycerin receptors (GlyRs), TRPV1 Receptors, and PPARs
- Endocannabinoids as Retrograde Messengers and How They Work in the Immune System, the Circulatory System, the Skeletal System, the Digestive System, the Reproductive System, and Connective Tissue (Fascia)
- Endocannabinoids in Pregnant Women
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Depletion and Cannabis Deficiency Syndromes like Anorexia Nervosa, Fibromyalgia, Huntington’s Disease, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Migraines, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s Disease, PTSD, and Schizophrenia
- Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome (CHS) and Cannabis Abstinence
Conditions Treated by Cannabis
Breaking down all of the most common ailments addressed by medical cannabis, and why it can be a useful treatment. The lesson covers these topics:
- Peer-Reviewed Research on Cannabis and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), including US Federal Government Restrictions on Cannabis Research and PubMed, the United States’ National Library of Medicine
- Cannabis Medical Information from licensed Cannabis physicians Dr. Joe Cohen, Dr. Arif Khan, and Dr. David Allen

- Palliative Cannabis Treatments and Symptoms Relieved by Cannabis, including Appetite Stimulation, Nausea and Vomiting Control, Intraocular Eye Pressure, Reducing Seizures, Reducing Pain and Inflammation, Reducing Chronic Pain, Movement Disorder Symptoms, Neurological Disorder Symptoms, Reducing Anxiety, Reducing Depression, Reducing Opioid Addiction
- Research on Cannabis Effects on Pain, Inflammation, CVD
- Cannabis vs. Prescription Pain Medicine, Opiates, Over-the-Counter Pain Medication, and Clobazam for Seizures
- CBD and THC Cannabis Treatment for Symptoms of Arthritis, Back Pain, Reflux Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome (RSDS), Depression, Migraines, Sleep Apnea, Neuropathy, Hypertension, Insomnia, ADD, Asthma, IBS, Spinal Cord Injury, PMS, Head Trauma, Bipolar Disorder, Substance Use Disorder, Fibromyalgia, Incontinence, Severe Itching (Pruritis), Psychotic Episodes, Sciatica, Shingles, Sports Injuries, Spinal Stenosis, Surgical Pain, Neuropathic Pain, Somatosensory System Pain, Herpes Pain, Multiple Sclerosis Pain and Muscle Spasms, and Vascular Disease Pain
- CBD and THC Cannabis Treatments for Geriatric Patients
- Double-Blind, Placebo Studies and Research about Medical Conditions Treated with Cannabis, including Joint Disorders, Alzheimer’s Disease, Senile Dementia, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s Disease, Neurodegenerative Disorders, Multiple Sclerosis and Cannabis, Lou Gehrig’s Disease, Movement Disorders, Epilepsy, Cancer, PTSD, Brain Injury (TBI), Stroke, Glutamate Excitotoxicity (GE), Neuromuscular Disease, Tourette’s Syndrome, Ataxia, Cerebral Palsy, Dystonia, Shy-Drager Syndrome, Paraplegia, Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS), Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), Periodic Limb Movement Disorder (PLMD), Tics, Tremors, Fear Extinction, Autoimmune Disease, Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), and Atherosclerosis
- The Role of CB2 Receptors in Heart Attacks, Strokes, Hardening of the Arteries, Heart Failure, and Cardiomyopathy
- Research on Cannabis as an Anti-Cancer Agent for Breast Carcinoma, Prostate Carcinoma, Colorectal Carcinoma, Gastric Adenocarcinoma, Skin Carcinoma, Leukemia, Glioblastomas, CNS Tumors, Lung Carcinoma, Uterine carcinoma, Thyroid Epithelioma, Pancreatic Carcinoma, Adenocarcinoma, Cervical Carcinoma, Oral Cancer, Biliary Tract Cancer, and Lymphoma
- Obesity and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), including CBD and Blood Glucose Levels
- Cannabis Treatment for Complex Conditions
- Cannabis as a Cytostatic and Apoptotic Cancer Treatment
- Cannabis Interactions with Chemotherapy Drugs
- Improving Health and Emotions with Cannabis
Administering Cannabis
Learn the best ways to consume cannabis and determine your dose, including side effects, drug interactions, and special patient populations. The lesson covers these topics:
- Cannabis Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability, Including Discussion of LDL Delivery, Nanoemulsions, Metabolites, and How Cannabis Gets You High
- First-Pass Metabolism Effects on THC, including the Difference Between THC and Hydroxy-THC and How THC Permeates the Blood-Brain Barrier
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Cannabis Administration Methods, including Ingestion, Inhalation, Sublingual, Buccal, Intraoral, Transdermals, Topicals, and Suppositories

- How Cannabis is Processed Depending on Administration Method
- Strength, Onset, and Duration of Cannabis Effects when Taken in Different Ways
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cannabis Edibles
- How Cannabis Edibles are Processed by the Body
- The Effects of Different Inhalation Methods, Including Smoking Buds, Vaporizing Flowers and Concentrates, Dabbing Cannabis, and Cannabis Inhalers
- Lung Cancer Risks of Smoking Cannabis
- How to Use Sublingual Cannabis, Cannabis Inhalers, Cannabis Patches, and Other Administration Methods
- Combining the Effects of Edibles and Sublingual Cannabis
- Transdermal Absorption, The Effect of Alcohol and Terpenes plus Transdermal Differences Between Cannabinoids
- Topical Cannabis Preparations including Phoenix Tears, Creams, Salves, Massage Oil, and Rectal and Vaginal Suppositories
- Raw Cannabis Juice as Medicine
- Finding the Right Cannabis Dose, including Genetic Testing, DNA Tests, Titration for New and Experienced Users
- Cannabis Sensitization Protocol and Cannabis Abstinence to Reduce Tolerance
- Avoiding the Negative Side Effects of Cannabis including Psychoactive Effects, Intoxication, Anxiety, Scattered Thinking, Mania, Hallucinations, Cardiovascular Side Effects (Increased Heart Rate and Decreased Blood Pressure), Fatigue, Drowsiness Sedative Effects, Insomnia, Changes in Dreams, Allergic Reactions, Cannabis Dependence, Dizziness, Cough, Decreased Appetite, Appetite Stimulation, Dry Mouth, Red Eyes, Increased Urination, Lack of Effects, and Vaginal Dryness
- Using Cannabis with Alternative Modalities such as: Cannabis and Yoga, Cannabis and Hypnosis, and Cannabis and Physical Therapy
- Cannabis Interactions with Other Drugs, including Medicinal Supplements, Cannabis and Opioids, Cannabis and Chemotherapy, Cannabis and NSAIDs, Cannabis and Acetaminophen, Cannabis and Steroids, Cannabis and Anti-Anxiety Medicine, Cannabis and Benzodiazepines, Cannabis and Probiotics, Cannabis and Alcohol, Cannabis and Antidepressants, Cannabis and Blood Pressure Medication, Cannabis and Warfarin, and Cannabis and Herbal Supplements
- Considerations for Geriatric, Pediatric, and Pregnant Medical Cannabis Patients
- Gender Differences in Cannabis Effects
Intro Cannabis Laws and Regulations
Cannabis Laws in the United States
A dive into cannabis laws across the US, including detailed information on current adult use, medical, and recreational programs in each state. The lesson covers these topics:
- Cannabis Laws in the United States, including United States Cannabis Regulation,
 Public Support for Cannabis in the US, Interaction between United States Federal and State Cannabis Laws, Cannabis Court Cases, Federal Cannabis Laws in the United States, Unwarranted Searches as They Relate to Cannabis, Firearms and Cannabis, and Cannabis and the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA)
Public Support for Cannabis in the US, Interaction between United States Federal and State Cannabis Laws, Cannabis Court Cases, Federal Cannabis Laws in the United States, Unwarranted Searches as They Relate to Cannabis, Firearms and Cannabis, and Cannabis and the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) - Medical Cannabis Programs in each US state
- Cannabis Possession, Distribution, Manufacturing, Growing, and Trafficking in Medical and Recreational Cannabis States
- Recreational Cannabis Programs in each US state
Cannabis Laws In Canada
With adult-use cannabis now legal nationwide, there has never been a better time to get involved in cannabis in Canada—but only if you understand the status of the Canadian cannabis laws. The lesson covers these topics:
- Cannabis Legalization for Personal Use in Canada, including the Cannabis Act
 , An Act Respecting Cannabis and to Amend the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, the Criminal Code, and Other Acts, and Adult Recreational Use
, An Act Respecting Cannabis and to Amend the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, the Criminal Code, and Other Acts, and Adult Recreational Use - Canada’s Federal Medical Cannabis Program, including Health Canada, Qualifying Conditions, and Becoming a Medical Cannabis Patient
- Canada’s Federal Cannabis Laws regarding Possession, Public Consumption, Distribution, Growing Cannabis, and Unlawful Activity
- Cannabis Possession, Public Consumption, Distribution, and Cultivation Laws in each Canadian province and territory
Handouts and Resources
Handouts and resources can be downloaded and/or accessed after enrollment ends.
- Definitions: Cannabis Basics Terminology
- Definitions: Cannabis Legal Terminology
- Definitions: Cannabis Business Terms
- Chart: Effects Of Common Cannabinoids
- Chart: Effects of Common Cannabis Terpenes
- Information Sheet: First Aid for Cannabis Side Effects
- Chart: Cannabis Interactions With Other Drugs
- Definitions: Cannabis Medical Terminology
- Information Sheet: Top Ten Symptoms Relieved By Cannabis
- MS Word Template: Cover Letter Builder
- MS Word Template: Resume Builder
- How to Become a Cannabis Budtender
- How to Become a Cannabis Dispensary Manager
- How to Become a Cannabis Expert
- How to Become a Marijuana Entrepreneur
- Sample: Cover Letter For Entry Level Grower
- Sample: Resume For Entry Level Grower
- Sample: Cover Letter For Dispensary Manager
- Sample: Resume For Dispensary Manager
- Sample: Blunt Royale Business Plan
- Sample: Blunt Royale Pitch Deck
- Supplemental Reading List: Cannabis Basics
- Procedure: Dab Equipment And How To Dab
- Chart: Cannabis Consumption Methods
- Chart: Entourage Effects
- Chart: Effects Of Common Cannabinoids On Receptors
- Checklist: Cannabis Industry Pitch Deck
- Checklist: Cannabis Industry Business Plan
- Procedure: 6-Day Cannabis Sensitization Protocol
- Procedure: Finding the Right Dose
- Supplemental Reading List: Cannabis As Medicine
- How To Become A Medical Cannabis Caregiver
- Chart: Characteristics Of Cannabis Types
- Chart: Storage For Cannabis Products
- Calculator: Cannabis Dry Weight Conversions
E-books
E-books can be accessed for the duration of your enrollment.
- Beyond Buds, Next Generation: Marijuana Concentrates and Cannabis Infusions
- Beyond Buds: Marijuana Extracts, Hash, Vaping, Dabbing, Edibles, and Medicines
- Big Book of Buds Greatest Hits
- Marijuana Garden Saver
- Marijuana Grower's Handbook
- Marijuana Harvest: Maximizing Quality & Yield in Your Cannabis Garden
- Branding Buds: The Commercialization of Cannabis
SNEAK PEEK
The Master of Cannabis Certificate Program takes you inside the cannabis industry. You will learn directly from Master's of marijuana in their field.
With your Medical Marijuana Certificate become qualified for these jobs:
Cannabis Caregiver
Cannabis Medical Personal
Medical Cannabis Consultant
CBD Consultant
Cannabis Patient Advocate
Marijuana/CBD Content Creator

James Y
Dearborn, MI
“
I had been wanting to learn how to open a medical marijuana dispensary for many years so I enrolled at CTU. I was amazed at the amount of legal information that was supplied for such a low cost. Thanks a lot.

FREE E-BOOK
DISPENSARY
7 Steps to Dispensary Ownership!
Open your own cannabis store!




 Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons
Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons  100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.
100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.