TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cannabis is a versatile plant that can grow in a variety of conditions, but it does have specific nutrient requirements that vary depending on the strain and the stage of growth.
Here, we’ll help you choose the right nutrient mix for your plants and experience level.
Nutrient Requirements for Cannabis
When it comes to growing cannabis in soil, it's important to understand the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients.
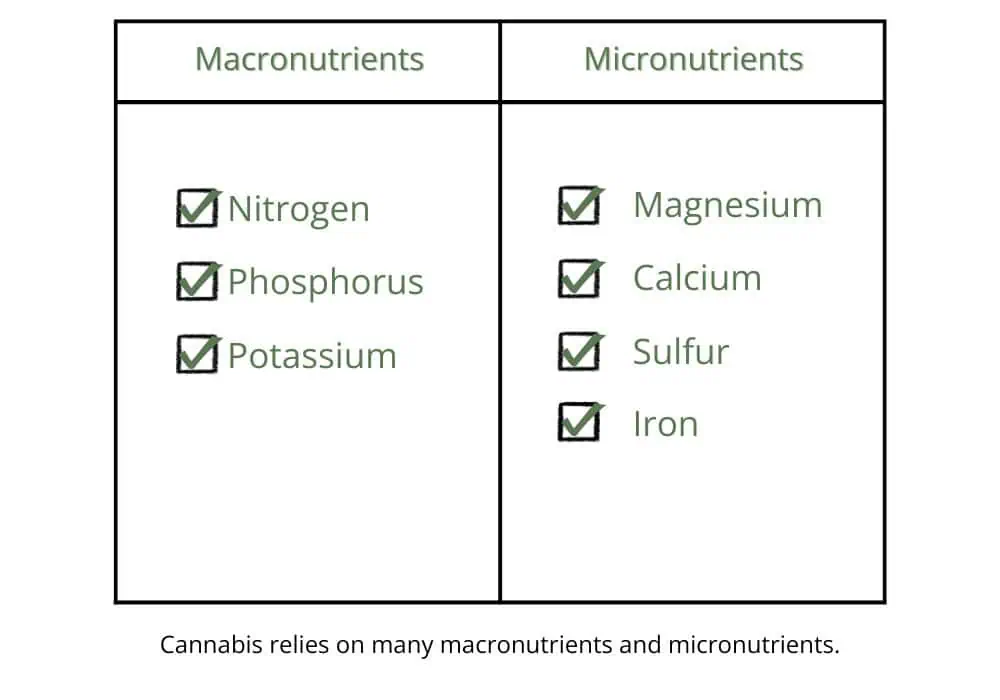
Cannabis requires both macronutrients (i.e. nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (i.e., calcium, sulfur, magnesium, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc) for successful growth.
Macronutrients are responsible for important functions such as photosynthesis, energy storage and transfer, and the development of strong roots and healthy foliage.
Micronutrients are responsible for functions such as enzyme production, chlorophyll formation, and overall plant metabolism.
Most commercially available soils have fertilizers and nutrients in them and will not usually require additional fertilizers and nutrients during the first month or two of growth.
Macro and Micronutrients
Marijuana plants depend on a set of essential elements in varying amounts. Nutrients needed in large amounts are called macronutrients, while micronutrients are needed in small amounts.
Feeding your plant the right amount of nutrients at the right time can prevent deficiencies.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is a critical macronutrient during the growing stage, especially the vegetative stage. Nitrogen enables chlorophyll to convert sunlight into energy, build proteins, and produce nucleic acid used by plant cells to replicate.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is another essential macronutrient that can help during the root formation to absorb all the necessary nutrients. Healthy roots are the foundation of strong cannabis stems, bud formation, and yield.
Potassium (K)
Potassium is known to aid in a plant’s water absorption. Potassium regulates the opening of the stomata, which are responsible for taking in CO2 and expelling water and oxygen. Potassium also helps produce ATP to make energy in the form of glucose for your plant.
NPK Ratio
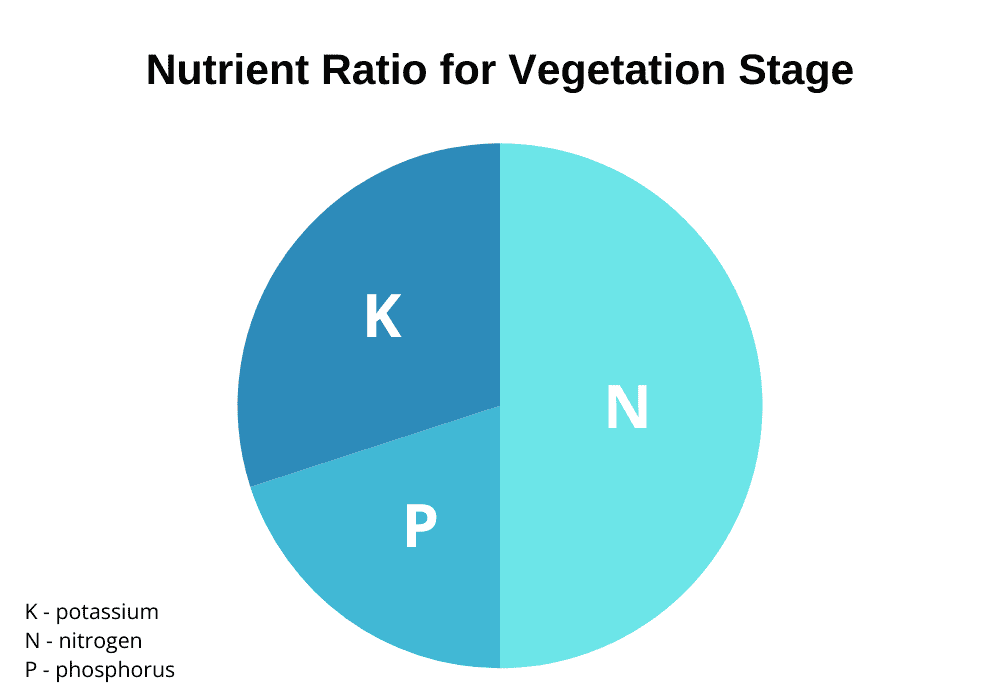
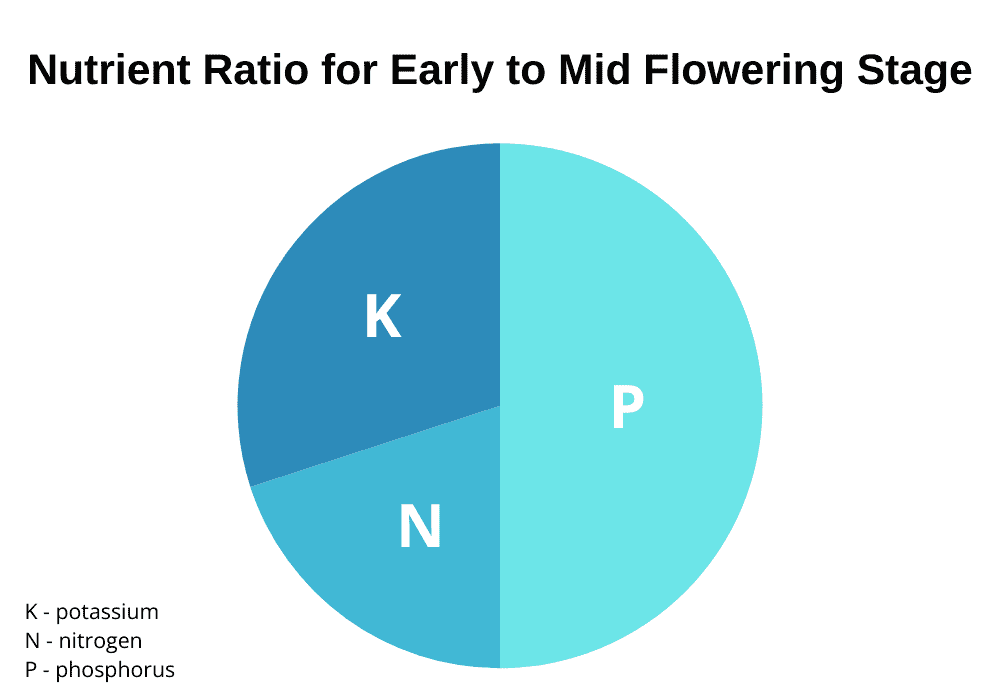
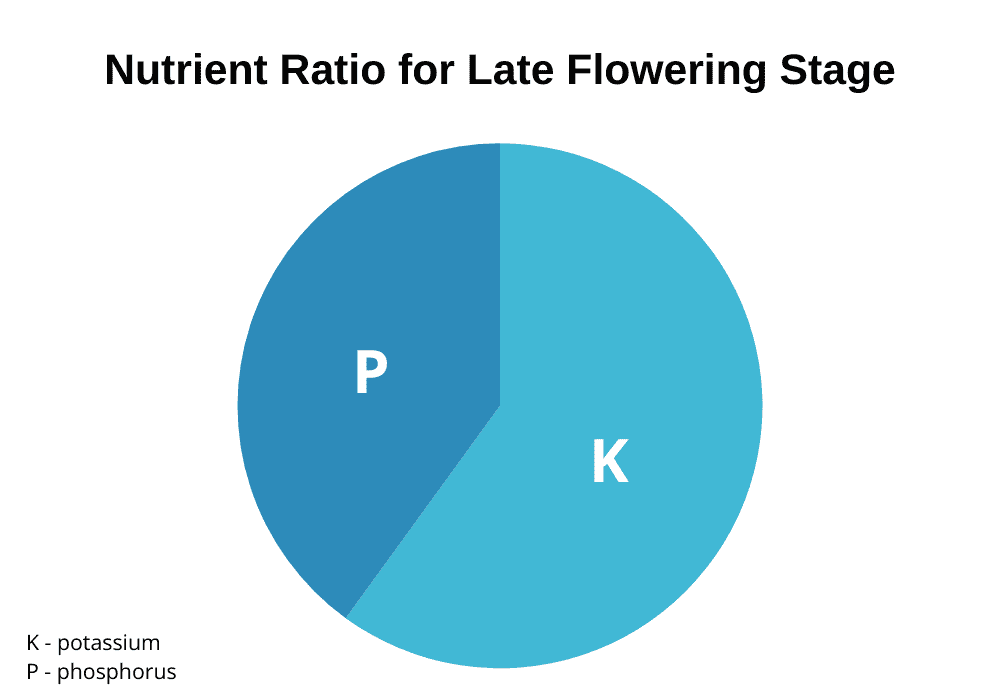
If you’re shopping for cannabis nutrient products, you’ll notice every bottle features three numbered signs such as 2-1-6, 5-0-1, 0-5-4, and so on. These numbers are the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, in that order.
It’s important to buy the right NPK ratio for different stages of plant growth. During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require a higher level of nitrogen. During the flowering phase, marijuana plants will require an increase in phosphorus.
Micronutrients for Cannabis
Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital micronutrient needed to help in the absorption of sunlight and the production of glucose needed for energy. Magnesium deficiencies can lead to yellow leaves, stem discoloration, and more.
Calcium
Calcium is another important micronutrient needed to support a plant’s cell walls. Calcium also aids in photosynthesis and the absorption of other nutrients.
Other Micronutrients
- Cobalt
- Sulfur
- Zinc
- Copper
- Silicon
- Boron
- Chlorine
- Manganese
- Iron
- Molybdenum
Cannabis Nutrients Deficiencies
Watch the plants closely for any changes or signs of nutrient deficiencies and disorders. Nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants can offer when the plant is not receiving the necessary nutrients to grow and thrive.
These deficiencies can manifest in various ways, including stunted growth, discoloration of leaves, and overall poor health. Some of the most common nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants include the following:
- Nitrogen deficiency: Nitrogen is an essential macronutrient that is necessary for the production of chlorophyll and the growth of leaves and stems. A nitrogen deficiency can result in the yellowing of the lower leaves and slow growth.
- Phosphorus deficiency: Phosphorus is essential for developing strong roots and healthy buds. A deficiency can result in slow growth, purple or reddish discoloration of the leaves, and small, poorly developed buds.
- Potassium deficiency: Potassium is necessary for regulating water balance and overall plant health. A deficiency can cause yellowing around the leaf edges, wilting, and a lack of resistance to pests and diseases.
- Iron deficiency: Magnesium is necessary to produce chlorophyll and overall plant metabolism. A deficiency can cause yellowing of the leaves, curled leaves, and lead to stunted growth.
It's important to note that the symptoms of nutrient deficiencies can be similar to those caused by other issues, such as pests or diseases, so it's important to properly diagnose the problem before attempting to treat it.
In addition, sometimes over-fertilization can lead to nutrient burn, which can cause similar symptoms as deficiency.
Soil-Based Products and Cannabis Nutrients

Organic fertilizers and additives that can be used in soil-based systems are:
Nitrogen Amendments
Ammonia – (NH3) is a gas containing 82% nitrogen, often used as a foliar feed in its aqueous form. It is a highly concentrated form of nitrogen and can be used to quickly boost the soul's nitrogen level. Use it with caution, as over application can lead to nutrient burn.
Cottonseed Meal -A byproduct resulting from oil extraction from cottonseed with a nitrogen content of 67%. Generally, it is used as a partial, slow-release nitrogen source in mixed fertilizers. It is also a good source of other nutrients such as potassium and phosphorus.
Blood Meal – Blood meal is a byproduct of the meatpacking industry and has a nitrogen content of 12 to 14%. The nitrogen is available quickly, but it does little for the mechanical properties of the soil.
Urea – Urea is a white crystalline compound containing 46% readily available nitrogen. This affordable form of nitrogen fertilizer is usually made from anhydrous ammonia (NH3) and is easy to handle, store and transport.
Fish Emulsion – Fish emulsion is prepared from non-edible fish and waste from fisheries. It has about 8% nitrogen. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and it is also a good source of micronutrients like zinc and iron.
Phosphate Amendments
Bone Meal – Two kinds: raw and steamed. Steamed bone meal has less nitrogen than raw, but more phosphoric acid. This material releases its nutrients slowly so it can be used without fear of injuring the crop.
Rock Phosphate – Mineral occurring in deposits throughout the world. Its effectiveness is dependant on its degree of fineness and the reaction of the soil. It's a slow-release fertilizer and it can take a long time to break down and become available to the plants.
Super Phosphate – A source of phosphoric acid in complete fertilizers and a direct treatment of soils deficient in phosphorous but well supplied with nitrogen and potassium. It's a fast-acting fertilizer and it's a good source of phosphorus, but it can cause an increase in soil pH.
Slag – Finely ground byproduct of steel manufacture. Its free lime content makes it of special value in the reclamation of acid soils. It's a slow-release fertilizer and it can help to improve soil structure.
Potassium Amendments
Wood ashes – Rapidly absorbable form of potassium that will raise pH because it is alkaline. It's important to be aware that wood ashes also contain high levels of salts that can be harmful if not used in moderation.
Seaweed – Contains a host of macro- and micro-nutrients, helps in water retention and absorption, and aids in weed prevention.
Growth and Flowering Supplements and Additives
There are more cannabis growth supplements, bloom supplements and stimulants, root stimulators and additives available than can be easily described here.
All supplements and additives must be added with caution to prevent any nutrient disorders, over-fertilization or nutrient burns. We will provide an overview of what is commonly available.
Fulvic Acid – used as a growth stimulator. Full acid is a natural acidic organic polymer that is extracted from humus found in soil, sediment, or aquatic environments.
Humic Acid – a principal component of humid substances, which are the major organic constituents of soil, peat, coal, many upland streams, lakes and ocean water. It is produced by biodegradation of dead organic matter. It is not a single acid; rather, it is a complex mixture of many different acids.
Gibberellic Acid – a hormone found in and extracted from plants. It is a naturally occurring plant growth regulator, which may cause a variety of effects including increasing the number and size of buds and the stimulation of seed germination.
Amino Acid – the key elements are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Amino acids are critical to life and have many functions in metabolism. One particularly important function is to serve as the building blocks of proteins.
Enzymes – proteins that increase or decrease the rates of chemical reactions. At this time there are limited products available that claim to promote the use of enzymes for improving and increasing the growth of medical cannabis.
Carbohydrates – plants require sugar and carbohydrates in order to have enough energy for intense flowering periods and rigorous growth. The logical solution would be to just add sugar to the nutrient solution right? Many have tried this and often molasses is used as a simple sugar additive. The problem with this is that the sugar is not as easily taken-in by plants in this form.
It is better to add a carbohydrate additive, which is designed to make these carbohydrate supplements easier for the plant to take in.
By using these additives, a grower can expect the plants to have sweeter tasting fruits, increase their essential oils, and nourish the plants to prepare them for intense flowering periods. If possible look for a carbohydrate additive that is organic, and combines easily with the rest of the nutrients being used.
Silica Based Products – promote healthier and stronger plant growth. When the roots take up silica, it is deposited in the cell walls of the plant as a solid, rigid ‘quartz-like' matrix. This produces a ‘mechanically’ stronger plant, which enables superior leaf orientation and therefore greater rates of photosynthesis and growth.
It increases the weight and shelf life of fruit due to the physical accumulation of silica in plant cells. Silica increases a plant's tolerance to heat stress or “wilting”. It also increases resistance to fungal diseases, particularly mildews and botrytis. It resists fungal ingress by accumulating around the points of fungal attack.
Silica improves the healing rate and neatness of pruning wounds. This property is especially beneficial in commercial cropping of plants such as medical cannabis. Regular pruning of these species threatens the plant's survival due to the risk of disease penetration through the site of the pruning wound.
Finally, silica increases a plant’s tolerance to nuisance chemicals such as sodium and chloride.
Vitamin Supplements – help a plant feel better when stressed and keep a plant healthy. Vitamins will help with resistance to fungal rots and insect attacks. While plants normally manufacture vitamins for themselves, if they have an external additional supply of them, they can then turn their energy to producing other elements they need, and thereby speed up growth.
Minerals – There are many minerals that are either required by the needs of the plant or are beneficial for improving the growth of the plant. Below are a few descriptions of minerals available for use.
Calcium-when added to the plants nutrient solution or to the soil it will improve the efficiency of nutrient uptake and encourage superior flowering.
Calcium – when added to the plant's nutrient solution or to the soil it will improve the efficiency of nutrient uptake and encourage superior flowering.
Citric Acids – can be added as a chelator (binder) for improved availability and plant uptake of nutrients and fertilizers.
Sulfur Based Additives – will activate enzymes, process compost and manure fertilizers, liberate roots systems and help balance soil pH.
Mycorrhiza – this is the relationship between the plant roots and beneficial fungi. Mycorrhizal products increase plant growth, nutrient and water uptake and improve soil structure.
Mixing Growing Medium (soil)
There are many commercially available soil mixes online or at a local grow supply stores that have been specifically developed for growing cannabis both indoors and outdoors.
For the experienced grower who chooses to mix their own soil, consider using this as a starting point for creating cannabis grow medium (soil):
“
There are over 300,000 jobs in the cannabis industry. CTU trained me for one of them!

Makes $24.50 @ THC +
- 50% Premium Potting Soil
- 20% Bat Guano High Phosphate Fertilizer
- 10% Organic Seafood Fertilizer
- 10% Perlite
- 05% Sand (optional)
- 05% Organic Mix roots, bark, etc.
Add more if a deficiency occurs in flowering. It is highly doubtful that it will, but if it does, use a diluted foliar feed.
- 3 lbs. Bone Meal
- 1 cup Dolomite Lime
- 2 tbsp. Humic acids are highly recommended.
Apply as recommended per the manufacturer's instructions.
- 5 lbs. Bat guano
- 2 five-gallon scoops of Perlite
It is recommended that all the ingredients be mixed together in a large barrel with a tight fitting lid, so as not to breathe in any dust or particles.
Roll the barrel around to mix the ingredients. If mixing the grow medium without a barrel with a lid and instead mixing the ingredients in an open container, a particle or dust mask must be worn.
Slightly moisten the ingredients to help avoid creating too much airborne dust and particles as the ingredients are mixed.
Start You Garden Today with Online Cannabis Training
Starting an indoor or outdoor cannabis garden can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience, but it is important to have a solid understanding of the plant's specific nutrient requirements. By enrolling at Cannabis Training University (CTU), you will gain the knowledge and skills needed to successfully grow your own cannabis.
CTU offers a wide range of courses for individuals of all experience levels, from beginner to advanced. Whether you are interested in growing cannabis for personal use or for a commercial operation, CTU's comprehensive curriculum will provide you with the training and resources you need to be successful.
To learn how to grow robust, healthy cannabis plants from seed to harvest, enroll in Cannabis Training University's marijuana courses.

Luis Cordova
Luis Cordova is a distinguished author, and renowned expert in cannabis cultivation, who possesses a Master's degree in Plant Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Science. As a valued contributor to highly esteemed publications such as Cannabis Training University and Maximum Yield Magazine, Luis has emerged as a trusted source of guidance and knowledge in the cannabis industry. Having written thousands of informative articles, Luis is widely recognized for his comprehensive expertise on cultivating cannabis, both indoors and outdoors.












 Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons
Jeff was involved in an accident where he endured a traumatic brain injury. He had a week-long stay in ICU where brain surgeons  100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.
100% risk free money back guarantee within 48 hours after purchase if student has not completed any of the courses or exams.